Lets write a C program to find smallest element in an array, without sorting the elements. And also print the position at which the smallest number is present in the array.
Related Read:
C Program To Find Biggest Element of An Array
Example: Expected Output
Enter 5 integer numbers
5
2
6
4
3
Biggest of 5 numbers is 2, at position 2.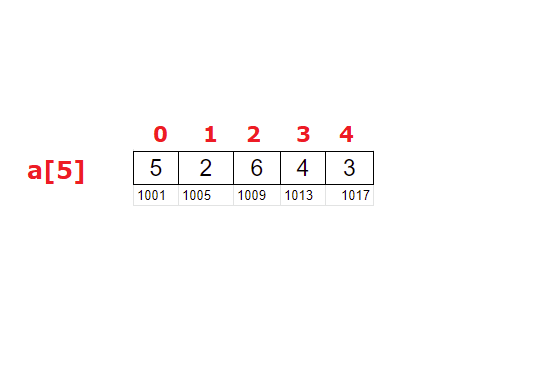
Video Tutorial: C Program To Find Smallest Element In An Array
[youtube https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0lnvlxKPD3A]
Source Code: C Program To Find Smallest Element of An Array
Method 1
#include<stdio.h>
#define N 5
int main()
{
int a[N], i, small, pos;
printf("Enter %d integer numbers\n", N);
for(i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
if(i == 0 || small > a[i])
{
small = a[i];
pos = i + 1;
}
}
printf("Smallest Number: %d, at position %d.\n", small, pos);
return 0;
}
Output 1:
Enter 5 integer numbers
9
8
6
2
5
Smallest Number: 2, at position 4.
Output 2:
Enter 5 integer numbers
5
6
1
3
2
Smallest Number: 1, at position 3.
Logic To Find Smallest Element In An Array
We ask the user to input N integer numbers. N being Macro, used to assign array size. In above source code N is assigned a value of 5. So user enters 5 integer numbers. While the user inputs numbers we check if it’s the first number input by the user. If its the first number/element, then we assign that first number/element entered by the user to variable small and assign 1 to variable pos, indicating that its the first element in the array.
Next, for each consecutive iteration of the for loop we check if the new value entered by the user is smaller than the value present in variable small. If it’s true, then we assign the new value entered by the user to variable small and also update the value of pos accordingly.
Once i < N condition is false, control exits for loop and we print the value present inside variable small and pos which will have smallest of N numbers or the smallest element of the array and position of that element in the array.
Explanation With Example
If int a[5] = {5, 2, 6, 4, 3};
for(i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
if(i == 0 || small > a[i])
{
small = a[i];
pos = i + 1;
}
}
| index | a[index] | small | pos = index + 1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | a[0] = 5 | 5 | 1 |
| 1 | a[1] = 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 2 | a[2] = 6 | ||
| 3 | a[3] = 4 | ||
| 4 | a[4] = 3 | ||
| 5 |
a[5] = {5, 2, 6, 4, 3}
small = 2;
pos = 2;
Source Code: C Program To Find Smallest Element of An Array
Method 2
#include<stdio.h>
#define N 5
int main()
{
int a[N], i, small, pos;
printf("Enter %d integer numbers\n", N);
for(i = 0; i < N; i++)
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
small = a[0];
pos = 1;
for(i = 1; i < N ; i++)
{
if(small > a[i])
{
small = a[i];
pos = i + 1;
}
}
printf("Smallest Number: %d, at position %d.\n", small, pos);
return 0;
}
Output 1:
Enter 5 integer numbers
9
8
6
2
5
Smallest Number: 2, at position 4.
Output 2:
Enter 5 integer numbers
5
2
6
4
3
Smallest Number: 2, at position 2.
Method 2: LOGIC
Here we accept N integer numbers from the user. Next we assign the first element of the array to variable small and 1 to pos. Now we use another for loop to loop through the array.
Inside for loop
Inside for loop we check if the value present inside variable small is greater or bigger than the value present at a[i]. If it’s true, then we assign the value of a[i] to small and value of (i+1) to variable pos.
At the end of for loop, variable small and pos will have smallest element of the array and the position at which this number is present in the array.
Note: Since we assign the value of first element of the array(which is present at location a[0]) to variable small, while comparing with other elements of the array, we start comparing from a[1] till a[N-1]. That’s the reason we’ve assigned initial value of i to 1 in the second for loop.
Since a[0] is assigned to variable small, there is no point in comparing big with a[0]. So we start comparison from a[1].
For list of all c programming interviews / viva question and answers visit: C Programming Interview / Viva Q&A List
For full C programming language free video tutorial list visit:C Programming: Beginner To Advance To Expert