Write a c program using pointers to find the smallest number in an array of 25 integers.
Pointers: A pointer variable is a variable which holds the address of another variable, of its own type.
Important Note:
1. Array elements are always stored in contiguous memory location.
2. A pointer when incremented always points to an immediately next location of its own type.
Related Read:
C Program To Find Smallest Element In An Array
Basics of Pointers In C Programming Language
Introduction To Arrays: C Programming Language
C Program To Find Smallest Element in An Array using Recursion
Important Video Tutorial
C Programming: Arrays, Pointers and Functions
Example: Expected Output
Enter 5 integer numbers
1
5
5
0
2
Smallest Element In The Array: 0
Visual Representation
Video Tutorial: C Program To Find Smallest Element in An Array using Pointers
[youtube https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bTDqhyaxPtE]
Source Code: C Program To Find Smallest Element in An Array using Pointers
#include<stdio.h>
#define N 5
int main()
{
int a[N], i, *small;
printf("Enter %d integer numbers\n", N);
for(i = 0; i < N; i++)
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
small = &a[0];
for(i = 1; i < N; i++)
{
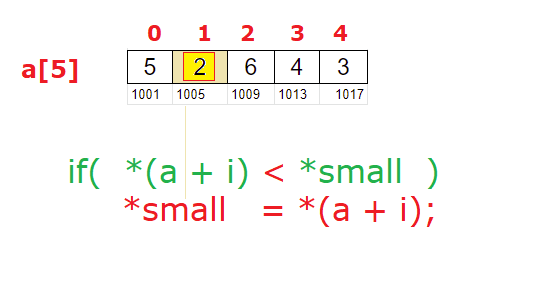
if( *(a + i) < *small)
*small = *(a + i);
}
printf("Smallest Element In The Array: %d\n", *small);
return 0;
}
Output:
Enter 5 integer numbers
5
2
6
4
3
Smallest Element In The Array: 2
Here we are assigning base address to pointer variable small.
Logic To Find Smallest Element In An Array using Pointers
We ask the user to input N integer numbers and store it inside a[N]. Next we assign base address to pointer variable small. Next we iterate through the array elements one by one using a for loop, and check if any of the elements of the array is smaller than whatever the value present at *small. If there is any element smaller than *small, we assign that value to *small.
Once the control exits the for loop, we print the value present in pointer variable *small, which holds the smallest element in the array.
Initializing *small to last elements address
#include<stdio.h>
#define N 5
int main()
{
int a[N], i, *small;
printf("Enter %d integer numbers\n", N);
for(i = 0; i < N; i++)
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
small = &a[N - 1];
for(i = 0; i < N - 1; i++)
{
if( *(a + i) < *small)
*small = *(a + i);
}
printf("Smallest Element In The Array: %d\n", *small);
return 0;
}
Output:
Enter 5 integer numbers
5
2
6
4
3
Smallest Element In The Array: 2
Here the logic is same, but we are assigning the address of last element of the array to pointer variable small.
Here we are simply making use of array variable for comparison
#include<stdio.h>
#define N 5
int main()
{
int a[N], i, *small;
printf("Enter %d integer numbers\n", N);
for(i = 0; i < N; i++)
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
small = &a[0];
for(i = 1; i < N; i++)
{
if( a[i] < *small)
*small = a[i];
}
printf("Smallest Element In The Array: %d\n", *small);
return 0;
}
Output:
Enter 5 integer numbers
2
1
3
4
5
Smallest Element In The Array: 1
As you can see in the above source code we are using array variable in if condition. But compiler converts a[i] to *(a + i). So internall a[i] is denoted as *(a + i) – which is *(base address + index).
Explanation With Example
N = 5;
a[N] = {5, 4, 6, 2, 3};
small = &a[0];
small = &a[0];
for(i = 1; i < N; i++)
{
if( *(a + i) < *small)
*small = *(a + i);
}
Here index variable i is initialized to 1. That is because pointer variable small has base address i.e., address of first element of the array. So we need not compare the value with itself. So we skip comparing it with a[0], and start the comparison from next index, which is 1.
| i | *(a + i) < *small | *small |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4 < 5 | 4 |
| 2 | 6 < 4 | 4 |
| 3 | 2 < 4 | 2 |
| 4 | 3 < 2 | 2 |
Smallest Element In The Array: 2
For list of all c programming interviews / viva question and answers visit: C Programming Interview / Viva Q&A List
For full C programming language free video tutorial list visit:C Programming: Beginner To Advance To Expert