Write a C program to shift elements of an array by n positions or rotate the array elements n times.
Example: Expected Input/Output
Input/Output
Enter 5 integer numbers
1
2
3
4
5
Enter the number of positions to shift
1
Enter the direction of shifting …
LEFT: 1 and RIGHT: 0
1
Array after shift operation …
2
3
4
5
1
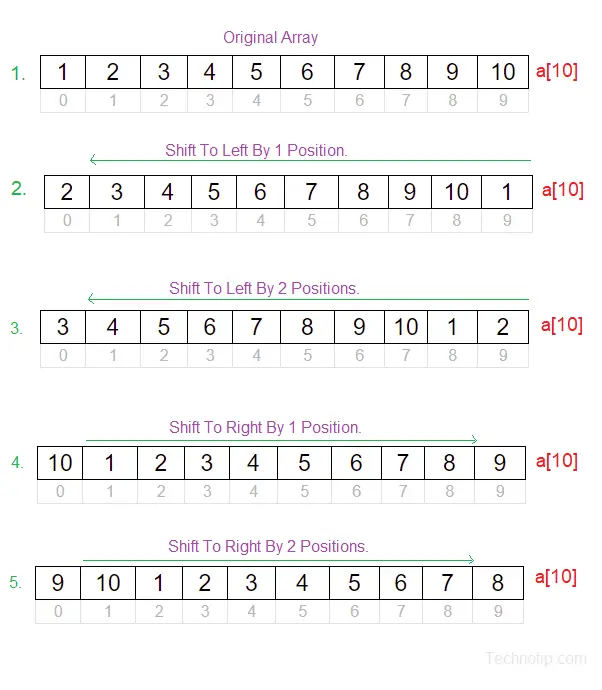
Visual Representation
Video Tutorial: C Program To Shift Elements of An Array by n Position
[youtube https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Fz-oyhu9Ccc]
Source Code: C Program To Shift Elements of An Array by n Position
#include<stdio.h>
#define N 5
int main()
{
int a[N], i, temp, pos, dir;
printf("Enter %d integer numbers\n", N);
for(i = 0; i < N; i++)
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
printf("Enter the number of positions to shift\n");
scanf("%d", &pos);
printf("Enter the direction of shifting ...\n");
printf("LEFT: 1 and RIGHT: 0\n");
scanf("%d", &dir);
while(pos)
{
if(dir)
{
temp = a[0];
for(i = 0; i < N - 1; i++)
a[i] = a[i + 1];
a[N - 1] = temp;
}
else
{
temp = a[N - 1];
for(i = N - 1; i > 0; i--)
a[i] = a[i - 1];
a[0] = temp;
}
pos--;
}
printf("Array after shift operation ...\n");
for(i = 0; i < N; i++)
printf("%d\n", a[i]);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
Output 1:
Enter 5 integer numbers
1
2
3
4
5
Enter the number of positions to shift
2
Enter the direction of shifting …
LEFT: 1 and RIGHT: 0
0
Array after shift operation …
4
5
1
2
3
Output 2:
Enter 5 integer numbers
1
2
3
4
5
Enter the number of positions to shift
2
Enter the direction of shifting …
LEFT: 1 and RIGHT: 0
1
Array after shift operation …
3
4
5
1
2
Logic To Shift Elements of An Array by n Position
First we ask the user to input N integer numbers and store it inside array variable a[N]. We then ask the user to input the number of positions to shift the elements of the array, and then the direction of shifting. If user inputs 1, then its LEFT shift, if user inputs 0, then its RIGHT shift operation.
Left Shift Operation
temp = a[0];
for(i = 0; i < N - 1; i++)
a[i] = a[i + 1];
a[N - 1] = temp;
If elements are shifted to left by 1 position, the first element which is present at a[0] will be lost. So we preserve it by transferring value present at a[0] to temp. Next we write a for loop.
We initialize 0 to i and iterate the “for loop” until i is less than (N – 1). Less than (N – 1) means it excludes the last element of the array present at index (N – 1) and that is because we’ll be storing the value present in variable temp to a[N – 1], after the execution of “for loop” completes.
Inside for loop, we transfer the value present at a[i + 1] to a[i]. That way we will be shifting elements of array to left by one position.
Right Shift Operation
temp = a[N - 1];
for(i = N - 1; i > 0; i--)
a[i] = a[i - 1];
a[0] = temp;
If elements are shifted to right by 1 position, the last element which is present at a[N – 1] will be lost. So we preserve it by transferring value present at a[N – 1] to temp. Next we write a for loop.
We initialize i to (N – 1) and iterate the “for loop” until i is greater than 0 and for each iteration we decrement the value of i by 1. Inside the “for loop” we assign a[i – 1] to a[i]. That is, we keep assigning the value backwards by 1 position. After completion of “for loop” execution, we assign the value of temp to the first index, which is a[0].
In “for loop” condition, we’re checking until i is greater than 0. That means, we’re not checking for i is equal to 0. That is because, at the end of “for loop” we assign the value present in temp to a[0].
While Loop
We put the whole logic of moving the elements to right and left inside of a while loop. While loop executes until variable pos is not equal to zero. Inside “while loop” we keep decrementing the value of i by 1 for each iteration. This way, we keep shifting the elements of the array by 1 position for every iteration of “while loop”. So if user wants to shift the elements to left by 2 positions, the entire “left shifting code/logic” will execute twice – moving the elements of the array 2 positions left.
For list of all c programming interviews / viva question and answers visit: C Programming Interview / Viva Q&A List
For full C programming language free video tutorial list visit:C Programming: Beginner To Advance To Expert
