Write a C program to find biggest element / number in an array using pointers and recursion.
We have covered both these logic in this video tutorial
1. Recursive function with no return type.
2. Recursive function with return type.
Related Read:
C Program To Find Biggest Element of An Array
Recursive Functions In C Programming Language
Basics of Pointers In C Programming Language
Introduction To Arrays: C Programming Language
Important Video Tutorial
C Programming: Arrays, Pointers and Functions
Example: Expected Output
Enter 5 integer number
5
2
6
4
3
Biggest Element in the array: 6
Visual Representation
Video Tutorial: C Program To Find Biggest Element In An Array using Recursion
[youtube https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-Cdp8QanJv8]
Source Code: Find Biggest Element of An Array using Recursion: With No Return Type
Method 1: With No Return Type
#include<stdio.h>
#define N 5
void biggest(int *num, int n, int big)
{
if(n < 0)
printf("Biggest element is %d\n", big);
else
{
if(*num > big)
big = *num;
biggest(++num, --n, big);
}
}
int main()
{
int a[N], i;
printf("Enter %d integer numbers\n", N);
for(i = 0; i < N; i++)
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
biggest(a, N - 1, a[0]);
return 0;
}
Output:
Enter 5 integer number
1
2
3
4
5
Biggest Element in the array: 5
Logic To Find Biggest Element of An Array using Recursion
We ask the user to enter N integer numbers and store it inside array variable a[N]. We pass base address(address of first element in the array) of the array, which is present in &a[0] or a, and last index of the array(indicating size of the array, from index 0), and first element of the array(assuming first element itself as big).
Inside Recursive function
Base Condition: This is the condition to terminate the recursive call. Here we check if the size of the array is less than zero. If it’s less than zero, then we display the value present inside variable big, which holds the biggest element in the array.
void biggest(int *num, int n, int big)
{
if(n < 0)
printf("Biggest element is %d\n", big);
else
{
if(*num > big)
big = *num;
biggest(++num, --n, big);
}
}
We need to take a pointer variable to accept the base address. Next we’ll have base condition. If base condition isn’t met – we check if the value present in variable big is less than value present at *num. If it’s true, then we transfer the value of *num to big. Next we increment the address of num by 1 and decrement the value of n by 1 and pass them to the same function along with the value of big. This is called recursive function call.
Once value of n is less than 0, we display the value of variable big, which holds the biggest element of the array.
Important Note:
1. Array elements are always stored in contiguous memory location.
2. A pointer when incremented always points to an immediately next location of its own type.
Source Code: Find Biggest Element of An Array using Recursion: With Return Value
Method 2: With Return Type
#include<stdio.h>
#define N 5
int biggest(int *num, int n, int big)
{
if(n < 0)
return big;
else
{
if(big < *num)
big = *num;
return biggest(++num, --n, big);
}
}
int main()
{
int a[N], i;
printf("Enter %d integer number\n", N);
for(i = 0; i < N; i++)
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
printf("Biggest Element in the array: %d\n", biggest(a, N - 1, a[0]));
return 0;
}
Output:
Enter 5 integer number
1
2
5
3
4
Biggest Element in the array: 5
After repeatedly incrementing value of num and decrementing the value n, we’ll reach a point where value of n will be less than 0. That’s when all the comparisons end, and variable big will have biggest element of the array. This result will be returned to the calling function, which in turn returns the result to the calling function and so on ..until the result is returned to the first function call, which was from with in main method – where we print the value of variable big.
Source Code: Using Array Variable In Recursive Function
Find Biggest Element of An Array using Recursion
#include<stdio.h>
#define N 5
int biggest(int num[], int n, int big)
{
if(n < 0)
return big;
else
{
if(big < num[n])
big = num[n];
return biggest(num, --n, big);
}
}
int main()
{
int a[N], i;
printf("Enter %d integer number\n", N);
for(i = 0; i < N; i++)
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
printf("Biggest Element in the array: %d\n", biggest(a, N - 1, a[0]));
return 0;
}
Output:
Enter 5 integer number
10
56
83
978
4
Biggest Element in the array: 978
Here we are taking array variable to receive the base address. We keep checking if a[n] is biggest than value present at variable big. If true, then we transfer a[n] value to variable big, and then recursively call the same function by decrementing the value of n by 1, and also pass the new value of big.
Once the value of n is less than 0, we return the value present in variable big, which holds the biggest element of the array.
Explanation With Example
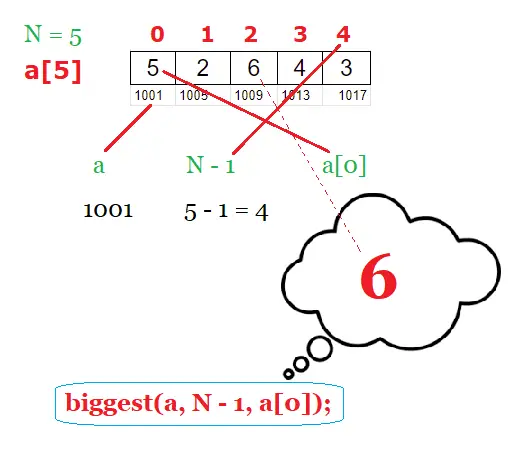
N = 5;
a[N] = {5, 2, 6, 4, 3};
n = N – 1 = 5 – 1 = 4;
num = a[0] = 5;
big = a[0] = 5;
biggest(num, --n, big);
| n | num[n] | big |
|---|---|---|
| 4 | 3 | 5 |
| 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 2 | 6 | 6 |
| 1 | 2 | 6 |
| 0 | 5 | 6 |
| -1 | 6 |
Biggest Element in the array: 6
For list of all c programming interviews / viva question and answers visit: C Programming Interview / Viva Q&A List
For full C programming language free video tutorial list visit:C Programming: Beginner To Advance To Expert