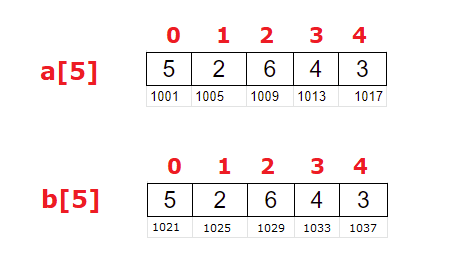
Lets write a c program to copy elements of one array to another array in reverse order. Hint: Make use of macros to assign size of the array. And both the arrays must have same size.
Related Read:
Basics of Arrays: C Program
Example: Expected Output
Enter 5 integer numbers
5
2
6
4
3
Copying elements from array a to b
In reverse Order
Original(a[5]) –> Copy(b[5])
5 –> 3
2 –> 4
6 –> 6
4 –> 2
3 –> 5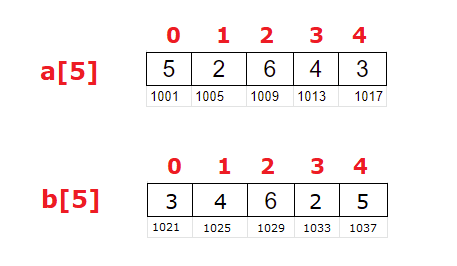
Video Tutorial: C Program To Copy Elements of One Array To Another In Reverse Order
[youtube https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UsIzctxViDs]
Source Code: C Program To Copy Elements of One Array To Another In Reverse Order
#include<stdio.h>
#define N 5
int main()
{
int a[N], b[N], i, j;
printf("Enter %d integer numbers\n", N);
for(i = 0; i < N; i++)
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
printf("\n\nCopying elements from array a to b, in reverse order\n");
for(i = N - 1, j = 0; i >= 0; i--, j++)
b[j] = a[i];
printf("\nOriginal(a[%d]) --> Copy(b[%d])\n", N, N);
for(i = 0; i < N; i++)
printf("%4d\t\t-->%6d\n", a[i], b[i]);
return 0;
}
Output:
Enter 5 integer numbers
1
2
3
4
5
Copying elements from array a to b, in reverse order
Original(a[5]) –> Copy(b[5])
1 –> 5
2 –> 4
3 –> 3
4 –> 2
5 –> 1
Logic To Copy Elements of One Array To Another In Reverse Order
We ask the user to enter N integer numbers. N is macro which is used to define size of the array. We store the user entered numbers inside array variable a. We initialize the variable i to last index of array a, and we initialize the variable j to first index of array variable b. Now for each iteration of the for loop, we assign the value of a[i] to b[j]. For each iteration of for loop we decrement the value of i by 1 and increment the value of j by 1. For loop iterates until i value is greater than or equal to 0.
At the end we print / display the content of both original array(a[5]) and the array to which the elements are copied to(b[5]) in reverse order.
Explanation With Example
If int a[5] = {5, 2, 6, 4, 3};
for(i = N - 1, j = 0; i >= 0; i--, j++)
b[j] = a[i];
| i | j | a[i] | b[j] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 0 | a[4] = 3 | b[0] = 3 |
| 3 | 1 | a[3] = 4 | b[1] = 4 |
| 2 | 2 | a[2] = 6 | b[2] = 6 |
| 1 | 3 | a[1] = 2 | b[3] = 2 |
| 0 | 4 | a[4] = 5 | b[0] = 5 |
a[5] = {5, 2, 6, 4, 3};
b[5] = {3, 4, 6, 2, 5};
For list of all c programming interviews / viva question and answers visit: C Programming Interview / Viva Q&A List
For full C programming language free video tutorial list visit:C Programming: Beginner To Advance To Expert