Write a C program to delete element of an array at user specified position. Show a confirmation message before deleting the element from specified position.
Related Read:
C Program To Shift Elements of An Array by n Position
Example: Expected Input/Output
Enter 5 integer numbers
10
12
14
16
18
Enter the position of the element to be deleted
2
You want to delete element 14 at position 2?
Yes: 1, No: 0
1
Array after deleting the specified element …
10
12
16
18
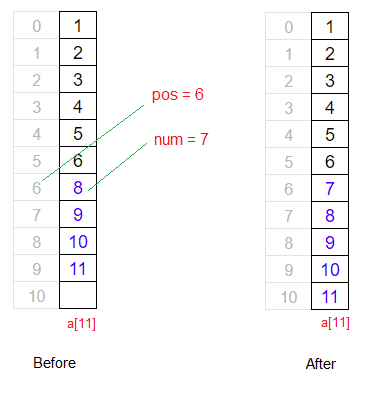
Visual Representation
Video Tutorial: C Program To Delete Element of An Array at Specified Position
[youtube https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VYGGJnQ1ArE]
Source Code: C Program To Delete Element of An Array at Specified Position
#include<stdio.h>
#define N 5
int main()
{
int a[N], i, pos, flag = 0;
printf("Enter %d integer numbers\n", N);
for(i = 0; i < N; i++)
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
do
{
printf("\nEnter the position of the element to be deleted\n");
scanf("%d", &pos);
if(pos >= N)
printf("\nPlease enter position within the range/size of the array\n");
else
{
printf("\nYou want to delete element %d at position %d?\n", a[pos], pos);
printf("Yes: 1, No: 0\n");
scanf("%d", &flag);
}
}while(flag == 0);
for(i = pos; i < (N - 1); i++)
a[i] = a[i + 1];
printf("\nArray after deleting the specified element ...\n");
for(i = 0; i < (N - 1); i++)
printf("%d\n", a[i]);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
Output 1:
Enter 5 integer numbers
1
5
9
7
3
Enter the position of the element to be deleted
4
You want to delete element 3 at position 4?
Yes: 1, No: 0
0
Enter the position of the element to be deleted
2
You want to delete element 9 at position 2?
Yes: 1, No: 0
1
Array after deleting the specified element …
1
5
7
3
Output 2:
Enter 5 integer numbers
1
2
3
4
5
Enter the position of the element to be deleted
15
Please enter position within the range/size of the array
Enter the position of the element to be deleted
0
You want to delete element 1 at position 0?
Yes: 1, No: 0
1
Array after deleting the specified element …
2
3
4
5
Logic To Delete Element of An Array at Specified Position
We ask the user to enter N integer numbers and store it inside array variable a[N]. Next we ask the index position of the element which has to be deleted from the array. Once we’ve these inputs from the user, we show a confirmation message to the user before deleting the specified element. Here user can either choose “1” to delete the element or choose “0” to re-select the element to be deleted.
If user selects “1” and chooses to delete the selected element, then we initialize i to the position of the element to be deleted. We iterate the for loop until i is less than (N – 1), and for each iteration we increment the value of i by 1.
Note: Observe the condition i < (N – 1), which is similar to writing i <= (N – 2). That is because we don’t want to swap/insert the last element of the array with some garbage value present outside the array limit/size.
Inside the for loop
Inside the ‘for loop’ we assign the element present in the next index to the current index element selected by i. i.e,. a[i] is assigned the value present at a[i + 1]. This way the value or the element present at the user selected position is lost, and the index N – 1 and N – 2 will have same elements. While displaying the array elements we leave the last index element, indicating deletion of 1 element from the array – so the array size has been obviously reduced by 1.
Note: Here array variable size isn’t reduced, but we simply do not display the last element of the array and create the illusion of reducing the size of array by 1.
Explanation With Example
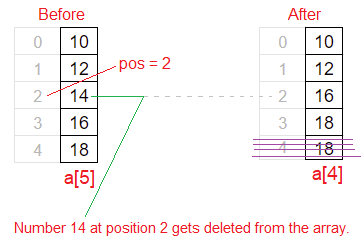
If a[5] = {10, 12, 14, 16, 18};
Delete element/number at position: 2
Element at user specified position: 14
for(i = pos; i < (N - 1); i++)
a[i] = a[i + 1];
We initialize i to user specified position, which is present in variable pos. Iterate this for loop until i in less than (N – 1), for each iteration increment the value of i by 1.
| i | pos | a[i] | a[i + 1] | a[i] = a[i + 1] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 2 | a[2] = 14 | a[3] = 16 | a[2] = 16 |
| 3 | 2 | a[3] = 16 | a[4] = 18 | a[3] = 18 |
| 4 | 2 | a[4] = 18 | – | – |
Now that index i is 4 and the array size is N = 5. So 4 < (5 – 1) is 4 < 4 which returns false, so the control exits the for loop. Using another “for loop” we display the array elements from index 0 to N – 2. i.e., from index i to i < (N – 1) or i <= (N – 2).
So the array elements after execution of above logic:
a[4] = {10, 12, 16, 18};
That’s how we successfully delete a element/number from user specified position 2.
For list of all c programming interviews / viva question and answers visit: C Programming Interview / Viva Q&A List
For full C programming language free video tutorial list visit:C Programming: Beginner To Advance To Expert