Lets write a C program to re-arrange even and odd elements of an array.
Note: We need to arrange EVEN numbers at the top and ODD numbers to the bottom of the same array.
Page Contents
Example: Expected Input/Output
Enter 5 integer numbers
11
10
13
12
15
After re-arranging even and odd elements …
10
12
13
11
15
Visual Representation
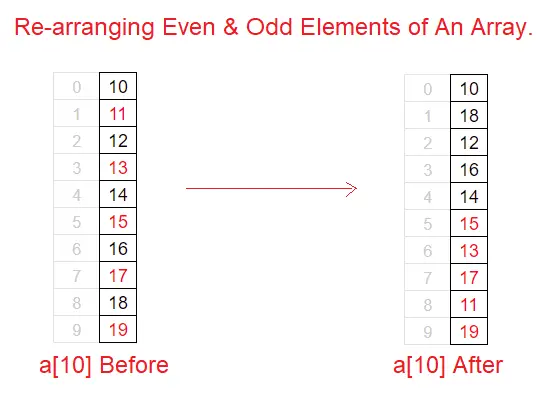
Video Tutorial: C Program To Re-arrange Even and Odd Elements of An Array
[youtube https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RfAdoYetz3M]
Source Code: C Program To Re-arrange Even and Odd Elements of An Array
#include<stdio.h>
#define N 10
int main()
{
int a[N], i, j = N, temp;
printf("Enter %d integer numbers\n", N);
for(i = 0; i < N; i++)
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
for(i = 0; i <= j; i++)
{
if(a[i] % 2 != 0)
{
while(j > i)
{
j--;
if(a[j] % 2 == 0)
{
temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
break;
}
}
}
}
printf("\nAfter re-arranging even and odd elements ...\n");
for(i = 0; i < N; i++)
printf("%d\n", a[i]);
return 0;
}
Output:
Enter 10 integer numbers
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
After re-arranging even and odd elements …
10
2
8
4
6
5
7
3
9
1
Logic To Re-arrange Even and Odd Elements of An Array
First we accept N integer numbers from the user and store it inside a[N]. Using “for loop” we iterate through the array elements one by one.
Inside For Loop
We initialize i to 0, which is the first index of any array. We iterate through this “for loop” until i is less than or equal to j. j represents the number of elements already sorted from bottom(N – 1) of the array. i.e., from index j to (N – 1) all the elements are already odd numbers. For each iteration of the for loop we increment the value of i by 1.
First if condition – inside for loop
Aim of our C program is to move all the even elements to top and odd elements to the bottom. So if the “for loop” selected element, which is present in a[i] already has a even number then we let that number stay there itself, and increment the value of i by one. If the “for loop” selected number, which is present in a[i] has odd number, then we start searching for a even number from the bottom of the same array to swap it with a[i].
Inside While loop
Assume that a[i] has a odd number. Now lets initialize j to the size of array, which is N. “While loop” executes until j is greater than i. Here i represents the number of elements already sorted from the top. i.e., from index 0 to i all the elements are already even numbers.
This “while loop” executes until j is greater than i. The value of i is set by “for loop”. It’s the index of the element which is selected by the “for loop”, which has ODD number. i.e., if the control has entered “while loop” that means a[i] has ODD number. “While Loop” checks for EVEN element from the bottom of the array to swap it with the ODD number present at a[i].
Second if condition – inside while loop
As soon as control enters the while loop we reduce the value of j by 1. So now j is (N – 1), which is the last element of any array. Next, if the “while loop” selected element, which is present at a[j] has EVEN number, then we swap that number with the ODD number present in a[i], and break out of the while loop.
For each iteration of “while loop” we decrement the value of j by 1. And we do not reset the value of j for each iteration of “for loop”.
Printing re-arranged array elements
Once control exits “for loop” we print the array elements from 0 to N -1 and it’ll have all EVEN numbers at the top and ODD numbers at the bottom.
Explanation With Example
If int a[5] = {11, 10, 13, 12, 15};
ODD: a[i] % 2 != 0
EVEN: a[j] % 2 == 0
j = N;
for(i = 0; i <= j; i++)
{
if(a[i] % 2 != 0)
{
while(j > i)
{
j--;
if(a[j] % 2 == 0)
{
temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
break;
}
}
}
}
| i | a[i] | ODD | j | a[j] | EVEN | Swap |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 11 | TRUE | 4 | 15 | FALSE | NO |
| 0 | 11 | TRUE | 3 | 12 | TRUE | YES |
| 1 | 10 | FALSE | 2 | 13 | FALSE | NO |
As you can see from above table swapping occurs at a[0] and a[3]. a[0] has integer number 11 and a[3] has integer number 12. So after swapping these numbers a[5] will be: {12, 10, 13, 11, 15}; So a[0], a[1] has EVEN numbers and a[2], a[3], a[4] has ODD numbers.
Important Note: i always represents the number of elements sorted from top(EVEN numbers), and j represents the index from (N – 1) which are sorted from bottom(ODD numbers).
For list of all c programming interviews / viva question and answers visit: C Programming Interview / Viva Q&A List
For full C programming language free video tutorial list visit:C Programming: Beginner To Advance To Expert
