Lets write a C program to find first and second biggest element/number in an array, without sorting it, and by using recursion.
Related Read:
Basics of Pointers In C Programming Language
Introduction To Arrays: C Programming Language
Important Video Tutorial
C Programming: Arrays, Pointers and Functions
Example: Expected Output
Enter 5 integer numbers
5
2
6
4
3
First Big: 6
Second Big: 5
Visual Representation
Video Tutorial: C Program To Find First and Second Biggest Element In An Array using Recursion
[youtube https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UqNZrOZa9u0]
Source Code: C Program To Find First and Second Biggest Element In An Array using Recursion
#include<stdio.h>
#define N 5
void fsBig(int *num, int n, int first, int second)
{
if(n < 2)
printf("First Big: %d\nSecond Big: %d\n", first, second);
else
{
if(*num > first)
{
second = first;
first = *num;
}
else if(*num > second && *num != first)
second = *num;
fsBig(--num, --n, first, second);
}
}
int main()
{
int a[N], i, first, second, count = 0;
printf("Enter %d integer numbers\n", N);
for(i = 0; i < N; i++)
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
for(i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
if(a[i] != a[0])
{
( (a[0] > a[i]) ?
(first = a[0], second = a[i]) :
(first = a[i], second = a[0]) );
break;
}
else
count++;
}
if(count == N)
{
printf("Biggest: %d\nSmallest: %d\n", a[0], a[0]);
return 0;
}
fsBig(&a[N - 1], N - 1, first, second);
return 0;
}
Output 1:
Enter 5 integer numbers
5
5
4
2
1
First Big: 5
Second Big: 4
Output 2:
Enter 5 integer numbers
5
5
5
5
5
Biggest: 5
Smallest: 5
Logic To Find First and Second Biggest Element In An Array using Recursion
We ask the user to enter N integer numbers and store it inside the address of array variable a[N]. Next we assign the biggest value between a[0] and a[1] to variable first and second biggest value to variable second. Then we pass the last elements address and length of the array and variables first and second to a function fsBig().
Inside function fsBig()
void fsBig(int *num, int n, int first, int second)
{
if(n < 2)
printf("First Big: %d\nSecond Big: %d\n", first, second);
else
{
if(*num > first)
{
second = first;
first = *num;
}
else if(*num > second && *num != first)
second = *num;
fsBig(--num, --n, first, second);
}
}
First we write the base condition or the termination condition: Once the length of the array or the variable n value is less than 2, we print the value present in variable fbig and sbig, and the control exits the function fsBig();
Note: We are checking till n < 2, because variables first and second already has values present at index 0 and 1, so need not compare them again against themselves.
Inside else block we write the actual logic to find the first and second biggest element in the array. First we check if the value present in pointer variable *num is greater than value present in variable fbig. If true, then there is a element which is bigger than fbig, that means, now whatever is present in fbig becomes second biggest element – so we transfer value present in fbig to sbig, and then transfer the new found biggest element of the array to variable fbig.
If a number is not greater than fbig, it can still be greater than sbig. So we check for that condition in else if. If its true, then we transfer the value of *num to sbig.
Recursive call
Next we call the same method fsBig() with new values. i.e., we reduce the address of num by 1, we reduce the value of index n by 1, and we pass the new values of fbig and sbig. This keeps on iterating until value of n is less than 2. Once the value of n is less than 2, the base condition is met and the control executes the printf() statement and exits the function fsBig().
Using array variable to receive base address from main method
#include<stdio.h>
#define N 5
void fsBig(int num[], int n, int first, int second)
{
if(n < 2)
printf("First Big: %d\nSecond Big: %d\n", first, second);
else
{
if(num[n] > first)
{
second = first;
first = num[n];
}
else if(num[n] > second && num[n] != first)
second = num[n];
fsBig(num, --n, first, second);
}
}
int main()
{
int a[N], i, first, second, count = 0;
printf("Enter %d integer numbers\n", N);
for(i = 0; i < N; i++)
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
for(i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
if(a[i] != a[0])
{
( (a[0] > a[i]) ?
(first = a[0], second = a[i]) :
(first = a[i], second = a[0]) );
break;
}
else
count++;
}
if(count == N)
{
printf("Biggest: %d\nSmallest: %d\n", a[0], a[0]);
return 0;
}
fsBig(a, N - 1, first, second);
return 0;
}
Output 1:
Enter 5 integer numbers
5
4
5
2
1
First Big: 5
Second Big: 4
Output 2:
Enter 5 integer numbers
5
5
4
4
2
First Big: 5
Second Big: 4
Here we do not alter the value of num while recursively calling the method fsBig(), as we compare with all the elements of the array by changing the value of index variable n.
Whenever we use array variable, compiler converts it to pointer as below
#include<stdio.h>
#define N 5
void fsBig(int num[], int n, int first, int second)
{
if(n < 2)
printf("First Big: %d\nSecond Big: %d\n", first, second);
else
{
if(*(num + n) > first)
{
second = first;
first = *(num + n);
}
else if(*(num + n) > second && *(num + n) != first)
second = *(num + n);
fsBig(num, --n, first, second);
}
}
int main()
{
int a[N], i, first, second, count = 0;
printf("Enter %d integer numbers\n", N);
for(i = 0; i < N; i++)
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
for(i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
if(a[i] != a[0])
{
( (a[0] > a[i]) ?
(first = a[0], second = a[i]) :
(first = a[i], second = a[0]) );
break;
}
else
count++;
}
if(count == N)
{
printf("Biggest: %d\nSmallest: %d\n", a[0], a[0]);
return 0;
}
fsBig(a, N - 1, first, second);
return 0;
}
Output:
Enter 5 integer numbers
1
2
3
5
5
First Big: 5
Second Big: 3
Whenever compiler encounters array variable like this a[i] or num[n] it converts it into *(a + i) and *(num + n).
i.e., Variable_name[array_index] = *(Base_address + array_index)
Note that, Variable_name holds Base_address. So Variable_name = Base_address.
Its faster to work with address than with variables. This example proves that arrays are pointers in disguise. i.e., arrays use pointers internally.
Explanation With Example
N = 5;
a[N] = {5, 4, 6, 2, 3};
first = 5;
second = 4;
n = N -1 = 5 – 1 = 4;
void fsBig(int num[], int n, int first, int second)
{
if(n < 2)
printf("First Big: %d\nSecond Big: %d\n", first, second);
else
{
if(*(num + n) > first)
{
second = first;
first = *(num + n);
}
else if(*(num + n) > second && *(num + n) != first)
second = *(num + n);
fsBig(num, --n, first, second);
}
}
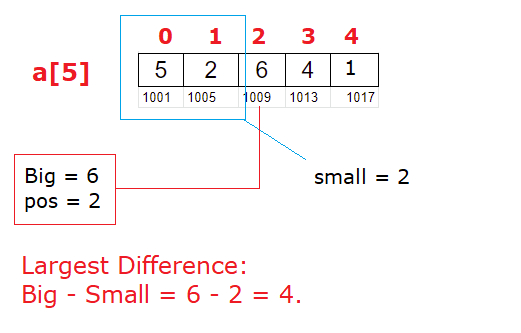
| n | num[n] | –n | fbig | sbig |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 4 |
| 3 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 4 |
| 2 | 6 | 1 | 6 | 5 |
First Big: 6
Second Big: 5
For list of all c programming interviews / viva question and answers visit: C Programming Interview / Viva Q&A List
For full C programming language free video tutorial list visit:C Programming: Beginner To Advance To Expert