Write a C program to segregate 0’s to the left and 1’s to the right of an array using counting method.
Related Read:
C Program To Segregate 0s and 1s In An Array using Swapping Method
Example: Expected Input/Output
Enter 10 elements(0 or 1)
1
0
0
1
1
1
1
0
0
1
Array after segregating o’s to left and 1’s to right
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
1
1
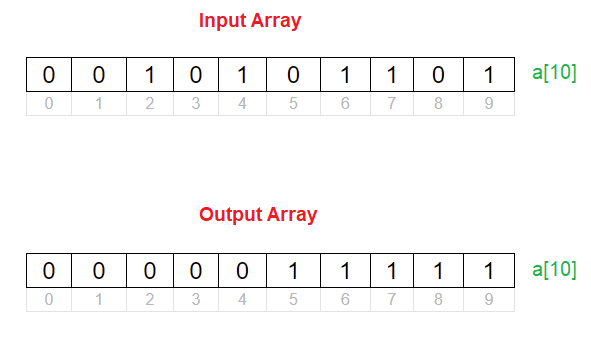
Visual Representation
Video Tutorial: C Program To Segregate 0’s and 1’s In An Array using Counting Method
[youtube https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gHW6WI-5724]
Source Code: C Program To Segregate 0’s and 1’s In An Array using Counting Method
#include<stdio.h>
#define N 5
int main()
{
int a[N], i, count = 0;
printf("Enter %d elements(0 or 1)\n", N);
for(i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
if(a[i] != 0 && a[i] != 1)
{
printf("Please enter only 0's and 1's as input\n");
i--;
}
else if(a[i] == 0)
count++;
}
for(i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
if(i < count)
a[i] = 0;
else
a[i] = 1;
}
printf("\nArray after segregating o's to left and 1's to right\n");
for(i = 0; i < N; i++)
printf("%d\n", a[i]);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
Output 1:
Enter 5 elements(0 or 1)
0
1
1
0
0
Array after segregating o’s to left and 1’s to right
0
0
0
1
1
Output 2:
Enter 5 elements(0 or 1)
2
Please enter only 0’s and 1’s as input
10
Please enter only 0’s and 1’s as input
1
0
2
Please enter only 0’s and 1’s as input
1
1
0
Array after segregating o’s to left and 1’s to right
0
0
1
1
1
Logic To Segregate 0’s and 1’s In An Array using Counting Method
We ask the user to input N integer numbers and store it inside a[N]. Next we iterate through each element of the array and if the user input is 0, then we increment the value of variable count by 1. After completing the iterations, variable count will have the number of 0’s input by the user.
Modifying the Array
Since user is allowed to either enter 0 or 1. So if we know the number of 0’s input by the user, we can easily calculate the number of 1’s in the array, using the formula:
N – count_0 = count_1
where, N is array size.
Now that we know the exact number of 0’s and 1’s input by the user, we re-enter the 0’s and 1’s as needed by the problem statement. That is, we arrange all the 0’s to left and 1’s to the right.
Number of 0’s plus the number of 1’s should be equal to the array size.
count_0 + count_1 = N;
Explanation With Example
If a[5] = {0, 1, 1, 0, 1};
| i | a[i] | count |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | |
| 2 | 1 | |
| 3 | 0 | 2 |
| 4 | 1 |
count = 2;
That is, the number of 0’s in user input array is 2. So the number of 1’s is:
array_size – count
5 – 2 = 3
So there are three 1’s and two 0’s.
for(i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
if(i < count)
a[i] = 0;
else
a[i] = 1;
}
Once we have this exact data. We can arrange Two 0’s from left of array, i.e., a[0] and a[1]. And three 1’s from a[2], a[3] and a[4].
This is how we segregate 0’s to left and 1’s to the right of an array, using counting method.
For list of all c programming interviews / viva question and answers visit: C Programming Interview / Viva Q&A List
For full C programming language free video tutorial list visit:C Programming: Beginner To Advance To Expert