Video tutorial illustrates the use of Primary Key, Foreign Key, Unique Key, AUTO_INCREMENT and NOT NULL in MySQL.
Primary Key
The PRIMARY KEY constraint uniquely identifies each record in a database table.
Primary keys have unique values.
Primary Keys are NOT NULL by default.
1 2 3 4 5 6 | CREATE TABLE Apple ( id int NOT NULL, name varchar(255) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY(id) ); |
Unique Key
The UNIQUE constraint uniquely identifies each record in a database table.
UNIQUE keys are not Primary Keys. but all Primary keys are Unique keys.
1 2 3 4 5 6 | CREATE TABLE Apple ( id int NOT NULL, name varchar(255) NOT NULL, UNIQUE(id) ); |
Foreign Key
A FOREIGN KEY in one table points to a PRIMARY KEY in another table.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | CREATE TABLE Orders ( id int NOT NULL, O_No int NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY(O_No), FOREIGN KEY(id) REFERENCES Apple(id) ); |
If your MySQL uses InnoDB engine, then use the following query:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | CREATE TABLE Orders ( id int NOT NULL, O_No int NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY(O_No), FOREIGN KEY(id) REFERENCES Apple(id) )ENGINE=InnoDB; |
Video Tutorial: Primary Foreign Unique Keys, AUTO_INCREMENT: MySQL
phpMyAdmin UI Interface Options
Options for assigning Primary key, unique key to the attributes..also the edit and delete keys.

AUTO_INCREMENT and NOT NULL
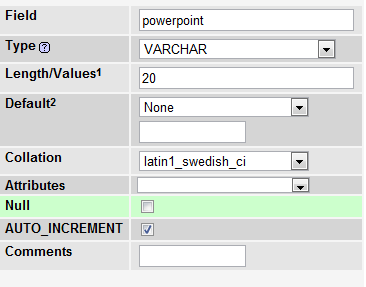
1 2 3 4 5 6 | CREATE TABLE Apple ( id int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, name varchar(255) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY(id) ); |
AUTO_INCREMENT is used for integer type data.. the advantage being, we need not explicitly send the data to this field. MySQL automatically inserts the value to this field.